Deep linking
This guide will describe how to configure your app to handle deep links on various platforms. To handle incoming links, you need to handle 2 scenarios:
- If the app wasn't previously open, the deep link needs to set the initial state
- If the app was already open, the deep link needs to update the state to reflect the incoming link
React Native provides a Linking to get notified of incoming links. React Navigation can integrate with the Linking module to automatically handle deep links. On Web, React Navigation can integrate with browser's history API to handle URLs on client side. See configuring links to see more details on how to configure links in React Navigation.
While you don't need to use the linking prop from React Navigation, and can handle deep links yourself by using the Linking API and navigating from there, it'll be significantly more complicated than using the linking prop which handles many edge cases for you. So we don't recommend implementing it by yourself.
Below, we'll go through required configurations so that the deep link integration works.
Setting up deep links
- Expo
- Community CLI
Configuring URL scheme
First, you will want to specify a URL scheme for your app. This corresponds to the string before :// in a URL, so if your scheme is example then a link to your app would be example://. You can register for a scheme in your app.json by adding a string under the scheme key:
{
"expo": {
"scheme": "example"
}
}
Next, install expo-linking which we'd need to get the deep link prefix:
npx expo install expo-linking
Then you can use Linking.createURL to get the prefix for your app:
const linking = {
prefixes: [Linking.createURL('/'),
};
See more details below at Configuring React Navigation. It is necessary to use The scheme specified in Why use
Linking.createURL?Linking.createURL since the scheme differs between the Expo Dev Client and standalone apps.app.json only applies to standalone apps. In the Expo client app you can deep link using exp://ADDRESS:PORT/--/ where ADDRESS is often 127.0.0.1 and PORT is often 19000 - the URL is printed when you run expo start. The Linking.createURL function abstracts it out so that you don't need to specify them manually.
If you are using universal links, you need to add your domain to the prefixes as well:
const linking = {
prefixes: [Linking.createURL('/'), 'https://app.example.com'],
};
Universal Links on iOS
To set up iOS universal Links in your Expo app, you need to configure your app config to include the associated domains and entitlements:
{
"expo": {
"ios": {
"associatedDomains": ["applinks:app.example.com"],
"entitlements": {
"com.apple.developer.associated-domains": ["applinks:app.example.com"]
}
}
}
}
You will also need to setup Associated Domains on your server.
See Expo's documentation on iOS Universal Links for more details.
App Links on Android
To set up Android App Links in your Expo app, you need to configure your app config to include the intentFilters:
{
"expo": {
"android": {
"intentFilters": [
{
"action": "VIEW",
"autoVerify": true,
"data": [
{
"scheme": "https",
"host": "app.example.com"
}
],
"category": ["BROWSABLE", "DEFAULT"]
}
]
}
}
}
You will also need to declare the association between your website and your intent filters by hosting a Digital Asset Links JSON file.
See Expo's documentation on Android App Links for more details.
Setup on iOS
Let's configure the native iOS app to open based on the example:// URI scheme.
You'll need to add the LinkingIOS folder into your header search paths as described here. Then you'll need to add the following lines to your or AppDelegate.swift or AppDelegate.mm file:
- Swift
- Objective-C
func application(_ app: UIApplication, open url: URL, options: [UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey : Any] = [:]) -> Bool {
return RCTLinkingManager.application(app, open: url, options: options)
}
#import <React/RCTLinkingManager.h>
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
openURL:(NSURL *)url
options:(NSDictionary<UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey,id> *)options
{
return [RCTLinkingManager application:application openURL:url options:options];
}
If your app is using Universal Links, you'll need to add the following code as well:
- Swift
- Objective-C
func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
continue userActivity: NSUserActivity,
restorationHandler: @escaping ([UIUserActivityRestoring]?) -> Void) -> Bool {
return RCTLinkingManager.application(
application,
continue: userActivity,
restorationHandler: restorationHandler
)
}
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application continueUserActivity:(nonnull NSUserActivity *)userActivity
restorationHandler:(nonnull void (^)(NSArray<id<UIUserActivityRestoring>> * _Nullable))restorationHandler
{
return [RCTLinkingManager application:application
continueUserActivity:userActivity
restorationHandler:restorationHandler];
}
Now you need to add the scheme to your project configuration.
The easiest way to do this is with the uri-scheme package by running the following:
npx uri-scheme add example --ios
If you want to do it manually, open the project (e.g. SimpleApp/ios/SimpleApp.xcworkspace) in Xcode. Select the project in sidebar and navigate to the info tab. Scroll down to "URL Types" and add one. In the new URL type, set the identifier and the URL scheme to your desired URL scheme.
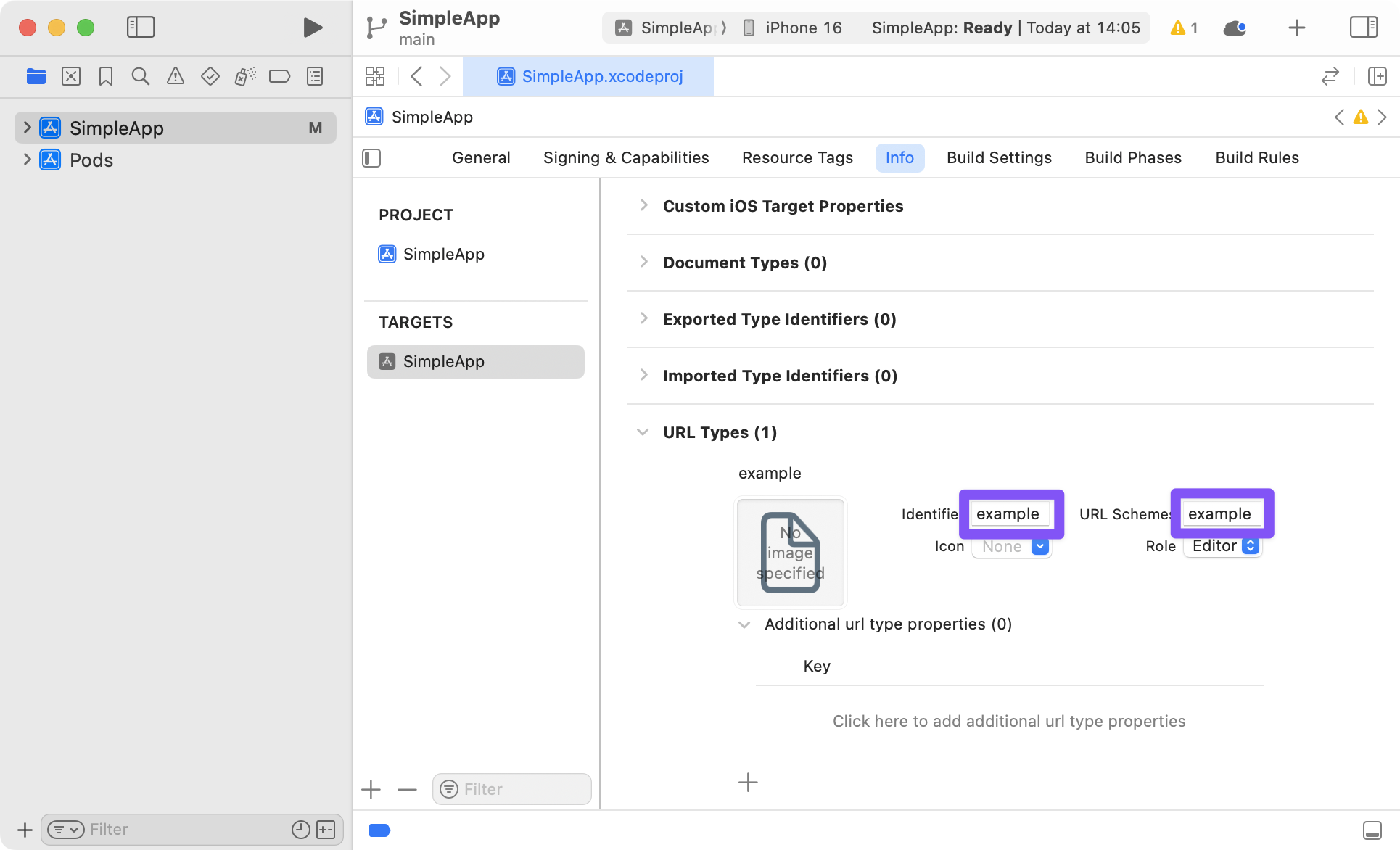
To make sure Universal Links work in your app, you also need to setup Associated Domains on your server.
Hybrid React Native and native iOS Applications
If you're using React Navigation within a hybrid app - an iOS app that has both Swift/ObjC and React Native parts - you may be missing the RCTLinkingIOS subspec in your Podfile, which is installed by default in new React Native projects. To add this, ensure your Podfile looks like the following:
pod 'React', :path => '../node_modules/react-native', :subspecs => [
. . . // other subspecs
'RCTLinkingIOS',
. . .
]
Setup on Android
To configure the external linking in Android, you can create a new intent in the manifest.
The easiest way to do this is with the uri-scheme package: npx uri-scheme add example --android.
If you want to add it manually, open up SimpleApp/android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml, and make the following adjustments:
- Set
launchModeofMainActivitytosingleTaskin order to receive intent on existingMainActivity(this is the default, so you may not need to actually change anything). - Add the new
intent-filterinside theMainActivityentry with aVIEWtype action:
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:launchMode="singleTask">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="example" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Similar to Universal Links on iOS, you can also use a domain to associate the app with your website on Android by verifying Android App Links. First, you need to configure your AndroidManifest.xml:
- Add
android:autoVerify="true"to your<intent-filter>entry. - Add your domain's
schemeandhostin a new<data>entry inside the<intent-filter>.
After adding them, it should look like this:
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:launchMode="singleTask">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="example" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="app.example.com" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Then, you need to declare the association between your website and your intent filters by hosting a Digital Asset Links JSON file.
Configuring React Navigation
To handle deep links, you need to configure React Navigation to use the scheme for parsing incoming deep links:
- Static
- Dynamic
const linking = {
prefixes: [
'example://', // Or `Linking.createURL('/')` for Expo apps
],
};
function App() {
return <Navigation linking={linking} />;
}
const linking = {
prefixes: [
'example://', // Or `Linking.createURL('/')` for Expo apps
],
};
function App() {
return (
<NavigationContainer linking={linking} fallback={<Text>Loading...</Text>}>
{/* content */}
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
If you are using universal links, you need to add your domain to the prefixes as well:
const linking = {
prefixes: [
'example://', // Or `Linking.createURL('/')` for Expo apps
'https://app.example.com',
],
};
See configuring links to see further details on how to configure links in React Navigation.
Testing deep links
Before testing deep links, make sure that you rebuild and install the app in your emulator/simulator/device.
If you're testing on iOS, run:
npx react-native run-ios
If you're testing on Android, run:
npx react-native run-android
If you're using Expo managed workflow and testing on Expo client, you don't need to rebuild the app. However, you will need to use the correct address and port that's printed when you run expo start, e.g. exp://127.0.0.1:19000/--/.
If you want to test with your custom scheme in your Expo app, you will need rebuild your standalone app by running expo build:ios -t simulator or expo build:android and install the resulting binaries.
Testing with npx uri-scheme
The uri-scheme package is a command line tool that can be used to test deep links on both iOS & Android. It can be used as follows:
npx uri-scheme open [your deep link] --[ios|android]
For example:
npx uri-scheme open "example://chat/jane" --ios
Or if using Expo client:
npx uri-scheme open "exp://127.0.0.1:19000/--/chat/jane" --ios
Testing with xcrun on iOS
The xcrun command can be used as follows to test deep links with the iOS simulator:
xcrun simctl openurl booted [your deep link]
For example:
xcrun simctl openurl booted "example://chat/jane"
Testing with adb on Android
The adb command can be used as follows to test deep links with the Android emulator or a connected device:
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d [your deep link] [your android package name]
For example:
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "example://chat/jane" com.simpleapp
Or if using Expo client:
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "exp://127.0.0.1:19000/--/chat/jane" host.exp.exponent
Integrating with other tools
In addition to deep links and universal links with React Native's Linking API, you may also want to integrate other tools for handling incoming links, e.g. Push Notifications - so that tapping on a notification can open the app to a specific screen.
To achieve this, you'd need to override how React Navigation subscribes to incoming links. To do so, you can provide your own getInitialURL and subscribe functions.
Here is an example integration with expo-notifications:
- Static
- Dynamic
const linking = {
prefixes: ['example://', 'https://app.example.com'],
// Custom function to get the URL which was used to open the app
async getInitialURL() {
// First, handle deep links
const url = await Linking.getInitialURL();
if (url != null) {
return url;
}
// Handle URL from expo push notifications
const response = await Notifications.getLastNotificationResponseAsync();
return response?.notification.request.content.data.url;
},
// Custom function to subscribe to incoming links
subscribe(listener) {
// Listen to incoming links for deep links
const linkingSubscription = Linking.addEventListener('url', ({ url }) => {
listener(url);
});
// Listen to expo push notifications when user interacts with them
const pushNotificationSubscription =
Notifications.addNotificationResponseReceivedListener((response) => {
const url = response.notification.request.content.data.url;
listener(url);
});
return () => {
// Clean up the event listeners
linkingSubscription.remove();
pushNotificationSubscription.remove();
};
},
};
const linking = {
prefixes: ['example://', 'https://app.example.com'],
// Custom function to get the URL which was used to open the app
async getInitialURL() {
// First, handle deep links
const url = await Linking.getInitialURL();
if (url != null) {
return url;
}
// Handle URL from expo push notifications
const response = await Notifications.getLastNotificationResponseAsync();
return response?.notification.request.content.data.url;
},
// Custom function to subscribe to incoming links
subscribe(listener) {
// Listen to incoming links for deep links
const linkingSubscription = Linking.addEventListener('url', ({ url }) => {
listener(url);
});
// Listen to expo push notifications when user interacts with them
const pushNotificationSubscription =
Notifications.addNotificationResponseReceivedListener((response) => {
const url = response.notification.request.content.data.url;
listener(url);
});
return () => {
// Clean up the event listeners
linkingSubscription.remove();
pushNotificationSubscription.remove();
};
},
config: {
// Deep link configuration
},
};
Similar to the above example, you can integrate any API that provides a way to get the initial URL and to subscribe to new incoming URLs using the getInitialURL and subscribe options.